How to Choose the Best Precast Formwork for Your Construction Project
In the ever-evolving landscape of construction, the choice of precast formwork plays a pivotal role in the efficiency and success of any project. According to John Smith, a leading expert in precast concrete technology, "Choosing the right precast formwork is essential for ensuring structural integrity and reducing project timelines." His insights shed light on the importance of selecting appropriate formwork systems that not only fit the architectural vision but also align with engineering requirements.
As construction projects become increasingly complex, the demand for innovative solutions like precast formwork rises. This method allows for faster construction times and improved quality control, making it a favored choice among industry professionals. However, navigating the various options available can be daunting. Factors such as project scale, design specifications, and budget constraints must all be taken into consideration. By carefully analyzing these elements, construction teams can identify the best precast formwork that meets their unique project needs.
Ultimately, the right precast formwork can significantly enhance the efficiency of construction operations, leading to cost savings and timely project completion. Understanding the key considerations and expert recommendations in this field is crucial for any construction manager aiming to leverage the full potential of precast solutions. As the industry continues to advance, informed decisions regarding precast formwork will be fundamental in shaping successful construction endeavors.
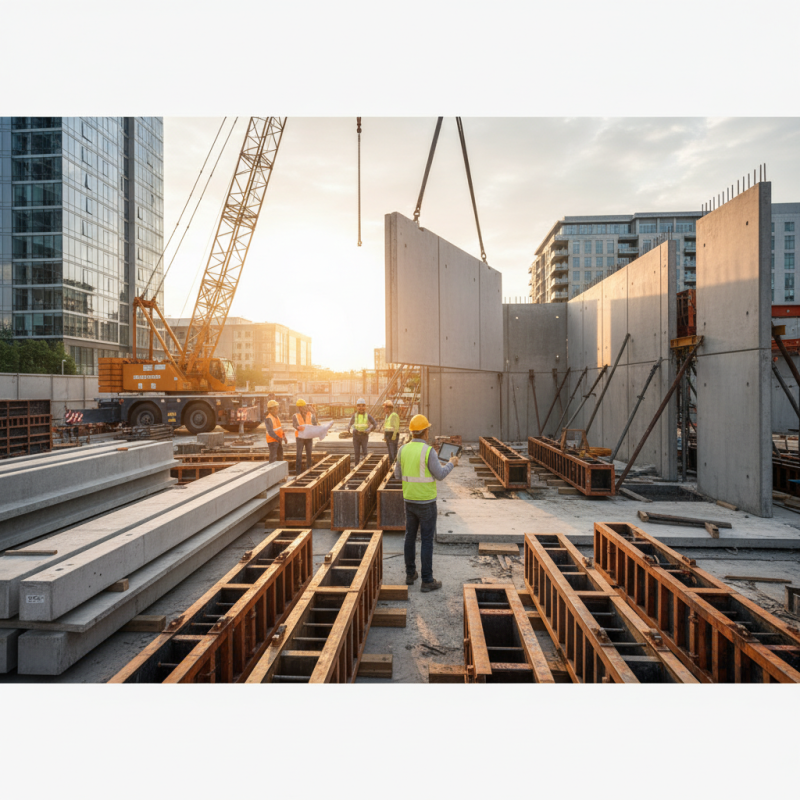

Factors Influencing the Selection of Precast Formwork Systems
When selecting precast formwork systems for construction projects, several key factors must be considered to ensure efficiency and effectiveness. First, assess the project's specific requirements, including the desired shape and size of the concrete elements. This understanding will help determine the type of formwork that can best accommodate the project’s structural needs. Additionally, consider the location and environmental conditions, as these factors influence the durability and suitability of the materials used in the formwork system.
Tips: Always evaluate the ease of installation and the speed of the formwork assembly process. A formwork system that can be quickly set up and dismantled will save time and reduce labor costs. It is also essential to consider the reusability of the formwork; systems that can be used for multiple projects not only help save costs in the long run but also contribute to a more sustainable construction approach.
Another important factor is the weight and handling requirements of the formwork. Lighter systems are generally easier to transport and can minimize the need for heavy lifting equipment, which can lead to safety enhancements on the job site. Furthermore, look at the available support resources and technical guidance from the manufacturers or suppliers, as proper support can significantly impact the installation and performance of the formwork in the long run.
Comparison of Common Precast Formwork Materials and Their Benefits
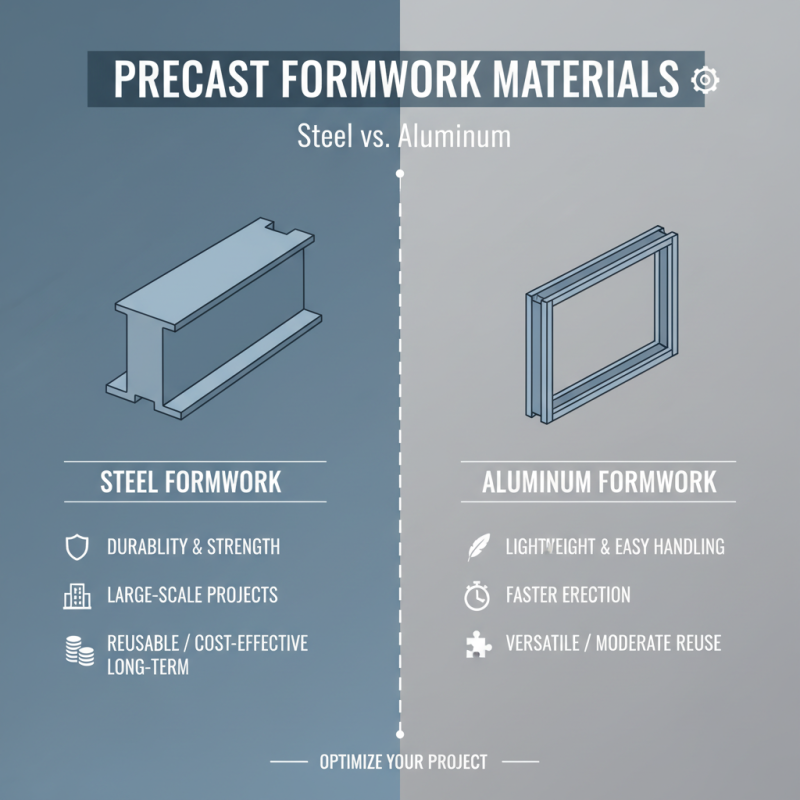
When selecting precast formwork for construction projects, understanding the common materials available can significantly impact efficiency, cost, and overall project success. Two prevalent options are steel and aluminum. Steel formwork is renowned for its durability and strength, making it ideal for large-scale projects that require high resistance to pressure and impact. Its capability to withstand harsh weather conditions further enhances its appeal. Additionally, steel can be reused multiple times, resulting in lower long-term costs despite a higher initial investment.
On the other hand, aluminum formwork offers a lightweight alternative that can facilitate quicker assembly and disassembly. This attribute is particularly advantageous for projects with tight timelines. Moreover, aluminum is resistant to corrosion, prolonging the lifespan of the formwork and ensuring clean finishes on concrete surfaces. While it may not bear the same strength as steel, the ease of handling and speed of execution can lead to significant labor cost savings. By weighing the benefits of each material, construction managers can make informed decisions that align with project goals and site-specific requirements.
Best Practices for Sizing and Engineering Precast Formwork
When selecting precast formwork for a construction project, proper sizing and engineering are critical to ensuring structural integrity and efficiency. According to a report by the Precast Concrete Institute, appropriately designed precast components can reduce construction time by up to 30%. This acceleration is largely due to the speed of assembly and the reduced need for in-situ curing, which underscores the importance of meticulous sizing and engineering practices. Precise measurements allow for optimal load distribution, minimizing the weight and maximizing the stability of the formwork during installation.
Best practices in sizing involve detailed consideration of the project's specific requirements, such as load-bearing capacity, environmental factors, and the intended design of the structure. Additionally, engineering analysis using finite element modeling can provide insights into how different designs perform under various conditions. A study published in the Journal of Construction Engineering and Management highlights that well-engineered precast systems can lead to a 20% decrease in material wastage, further supporting the economic viability of the project. Investing time in these preliminary evaluations not only enhances safety but also optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that the precast formwork effectively supports the goals of the construction project.
Cost Implications of Various Precast Formwork Options in Construction
The selection of precast formwork plays a crucial role in the overall cost management of construction projects. According to a report by the American Concrete Institute, utilizing precast concrete can lead to a reduction in labor costs by up to 30% compared to traditional cast-in-place methods. This reduction is primarily due to the faster installation times and minimized on-site labor required when using standardized precast forms. Additionally, the inherent efficiency of precast construction lessens the need for extensive scaffolding and other ancillary equipment, further driving down costs.
Various precast formwork options come with distinct cost implications that project managers must carefully evaluate. For example, while traditional precast concrete panels may have a higher upfront cost, their durability and lower maintenance expenses over time can yield significant savings in the long run. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology found that investing in higher-quality precast materials could result in lifetime savings of 20% to 30% due to reduced repair and replacement costs. Conversely, opting for lower-cost, less durable options might save initial expenses but could lead to increased lifecycle costs, undermining the financial advantages of the project. Thus, a comprehensive cost analysis, factoring both short-term investments and long-term implications, is essential when selecting the most suitable precast formwork for any given construction endeavor.
Cost Implications of Various Precast Formwork Options in Construction
Key Safety Standards and Regulations for Precast Formwork Use
When selecting precast formwork for construction projects, understanding the key safety standards and regulations is paramount. Precast formwork must conform to industry-specific guidelines that ensure structural integrity and worker safety. These regulations often include specifications regarding material strength, load-bearing capacities, and installation procedures. Adhering to such standards not only mitigates risks during construction but also promotes a safer working environment for all personnel involved.
Moreover, regulatory bodies may dictate the necessary inspections and certifications required before the precast formwork can be employed. Compliance with local building codes and safety regulations is essential, as it helps in preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of the structure. Engaging with trained professionals who are knowledgeable about these safety standards can further enhance the selection process and implementation, aligning the construction project with best practices while safeguarding the health and safety of the workers on site.
How to Choose the Best Precast Formwork for Your Construction Project
| Dimension | Description | Safety Standard | Regulation Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Capacity | The maximum load the formwork can support during construction. | EN 12811 | European Committee for Standardization |
| Fire Resistance | Ability to withstand fire exposure without collapsing. | UL 263 | Underwriters Laboratories |
| Environmental Impact | Assessment of the ecological footprint during the lifecycle. | ISO 14001 | International Organization for Standardization |
| Worker Safety | Measures to protect workers during installation and removal. | OSHA Regulations | Occupational Safety and Health Administration |
| Durability | Ability to withstand weather and wear over time. | ASTM C1602 | American Society for Testing and Materials |
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Precast Concrete Formwork for Your Project
-

How to Choose the Right Steel Formwork for Your Construction Project
-
How to Choose the Right Circular Column Formwork for Your Construction Project
-
Why Bulkhead Formwork is Essential for Successful Construction Projects
-

Top 10 Things You Should Know About Formwork for Construction Projects
-

How to Choose the Right Bracing Formwork for Your Construction Project